Amazon DynamoDB Uses and Benefits: Unveiling Modern Application Possibilities
Amazon DynamoDB, a managed NoSQL database service, has gained substantial popularity in the realm of modern web applications. In this article, we’ll unravel the complexities of Amazon DynamoDB, exploring what it is and how it’s utilized across a variety of use cases.
Understanding Amazon DynamoDB
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed, serverless NoSQL database offered by Amazon Web Services (AWS). NoSQL databases are designed to handle vast amounts of unstructured or semi-structured data, offering flexibility and scalability beyond traditional relational databases.
Key Features of Amazon DynamoDB:
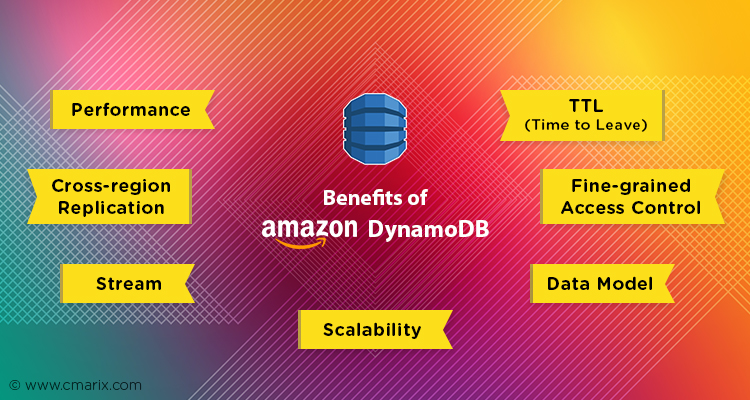
- Scalability: DynamoDB is known for its seamless scalability. It automatically scales up or down based on the application’s demands, ensuring consistent performance.
- High Availability: DynamoDB replicates data across multiple Availability Zones to provide high availability and durability.
- Low Latency: With its distributed architecture, DynamoDB delivers low latency even for high-demand applications.
- Fully Managed: AWS takes care of provisioning, scaling, backups, and maintenance, allowing developers to focus on application logic.
Common Use Cases of Amazon DynamoDB:
- Real-Time Applications: DynamoDB is ideal for applications requiring real-time data access and updates. Examples include gaming leaderboards, social media feeds, and messaging platforms.
- E-Commerce: Online retailers utilize DynamoDB to manage catalog information, customer profiles, and order histories, ensuring efficient and seamless shopping experiences.
- Internet of Things (IoT): DynamoDB’s ability to handle large volumes of data and fast-paced updates makes it suitable for IoT applications, such as sensor data collection and monitoring.
- Content Management Systems: Websites and applications with user-generated content benefit from DynamoDB’s ability to manage variable data structures.
- Analytical Workloads: DynamoDB can be part of an architecture that supports both operational and analytical workloads, where data is ingested from DynamoDB into data warehousing solutions for analysis.
- Session Management: Web applications use DynamoDB to store user sessions and maintain state, even when distributed across multiple instances.
Getting Started with Amazon DynamoDB:
- Creating Tables: Tables are the primary data storage units in DynamoDB. Define attributes, set primary keys, and specify the desired capacity units.
- Data Management: Use the AWS SDKs or APIs to interact with DynamoDB programmatically. CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) are straightforward to execute.
- Scaling: DynamoDB offers two capacity modes: on-demand and provisioned. Choose the one that best suits your application’s needs.
Amazon DynamoDB is a versatile and powerful database solution that plays a pivotal role in modern application development. Its flexibility, scalability, and managed nature make it an attractive choice for various use cases across industries. As you embark on your journey with DynamoDB, consider the specific needs of your application and leverage its features to deliver seamless and responsive experiences to your users.