Maximizing Uptime: Understanding Azure Availability Sets for Virtual Machine High Availability
In the ever-evolving world of cloud computing, achieving high availability and reliability of applications is paramount. Azure Availability Sets emerge as a powerful feature within Azure virtual machines, offering users a robust solution to minimize the impact of both planned and unplanned maintenance events. This article delves into the intricacies of Azure Availability Sets, shedding light on fault domains, update domains, and their pivotal roles in ensuring the continuous operation of virtual machines.
Deciphering Fault Domains and Update Domains
To comprehend Azure Availability Sets, one must first grasp the concepts of fault domains and update domains:
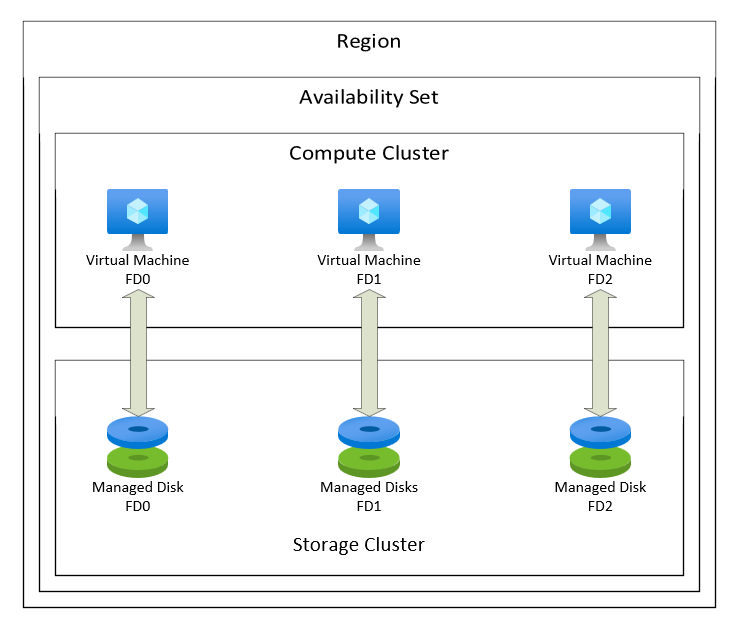
- Fault domains: These represent groups of virtual machines that share a common power source and network switch. In the unfortunate event of a hardware failure or power outage within a fault domain, all virtual machines in that group are affected. To mitigate the risk of simultaneous failures, Azure disperses virtual machines in an availability set across different fault domains. Typically, each availability set consists of three fault domains, although users can configure up to five fault domains depending on the region and availability set type.
- Update domains: Update domains, on the other hand, encompass groups of virtual machines and the underlying physical hardware that can be rebooted or updated simultaneously. During planned maintenance, Azure proceeds one update domain at a time, ensuring that only a subset of virtual machines in an availability set is impacted, while the rest continue their operations seamlessly. By default, each availability set is divided into five update domains, although customization up to 20 update domains is possible based on region and availability set type.
Working of Fault Domains and Update Domains
Upon creating an availability set, users specify the desired number of fault domains and update domains for their virtual machines. Azure subsequently assigns each virtual machine to a fault domain and update domain following these principles:
- Each virtual machine belongs to one fault domain and one update domain.
- Azure strives to distribute virtual machines evenly among fault domains and update domains, except when the number of virtual machines isn’t divisible by the chosen domain count.
- Assignment of virtual machines to fault domains and update domains is random and independent. Therefore, two virtual machines in the same fault domain may belong to different update domains and vice versa.
For example, VM1 might belong to fault domain 0 and update domain 0, while VM2 may belong to fault domain 1 and update domain 1.
This assignment configuration influences how Azure schedules updates across virtual machines concerning their update and fault domains. During planned maintenance:
- Azure selects one update domain for reboot or update at a time, although the order may not follow a strict sequence.
- Users are notified of planned maintenance events and provided with a self-maintenance window, granting them control over when maintenance takes place, typically within 35 days.
- If users do not initiate maintenance within the self-maintenance window, Azure triggers it automatically at a random time within the allocated period.
- During maintenance, Azure briefly pauses or reboots virtual machines within the selected update domain. Most virtual machines experience this operation in less than 10 seconds, with some larger or specialized instances requiring up to 30 seconds.
- After the pause or reboot, Azure resumes or restarts virtual machines, ensuring synchronization with the host time.
- Azure repeats these steps for each update domain until all virtual machines in the availability set are updated.
This approach ensures that only a fraction of virtual machines within an availability set are affected by planned maintenance at any given time, while others continue to run smoothly, serving the application. By minimizing downtime and disruption, Azure achieves high availability and reliability.
Unveiling the Power of Microsoft Access Database Engine 2016 Redistributable
However, high availability isn’t solely about planned maintenance; unplanned events, such as hardware failures, power outages, or network issues, can also disrupt virtual machines. Azure addresses these concerns by using fault domains to isolate and distribute virtual machines across distinct physical locations within an Azure datacenter. In case of an unplanned event within one fault domain, only virtual machines in that domain are affected, leaving those in other domains unscathed. This distribution reduces the risk of simultaneous failures, further boosting application availability.
The Significance of Fault Domains and Update Domains for High Availability
Fault domains and update domains play a pivotal role in achieving high availability for virtual machines by enabling users to:
- Mitigate the impact of planned maintenance: Update domains ensure that only a subset of virtual machines within an availability set undergoes planned maintenance at any given time, allowing others to operate undisturbed. Users can even control when and how maintenance occurs through self-maintenance windows or automation with Azure Automation.
- Safeguard against simultaneous failures: Through fault domains, virtual machines are distributed across diverse physical locations within an Azure datacenter. Consequently, if a hardware failure or power outage occurs within one fault domain, only virtual machines in that domain are affected, minimizing the overall risk of concurrent failures.
- Fulfill the Azure SLA: Utilizing availability sets with multiple virtual machines spanning different fault domains and update domains enables users to meet the 99.95% Azure SLA (Service Level Agreement) for virtual machine connectivity. This assurance guarantees that at least one virtual machine in an availability set will be available for use 99.95% of the time.
Azure Availability Sets serve as an invaluable feature within Azure virtual machines, empowering users to achieve unprecedented levels of high availability and reliability. By skillfully managing planned and unplanned maintenance events, Azure Availability Sets ensure seamless application operation. Fault domains and update domains act as the cornerstones of this architecture, distributing virtual machines strategically and minimizing disruptions. This approach allows businesses to meet stringent SLAs and provide uninterrupted services to their customers.